
- #How does an analog to digital converter work full
- #How does an analog to digital converter work series
The number of analog to digital conversions the converter can make every second is called the sample speed. ADCs up to 24 bits are available, though conversion frequencies are low, in the order of a few hertz. This can be prevented by using an ADC with a higher resolution. What if the voltage changes are below the 4.9mV per step? This puts the ADC in a dead zone, the conversion result therefore always has a small error. This measure of ‘volts per bit’ is called the resolution of the ADC. So each binary step up represents around 4.9mV, since there are 1024 possible digits in 10 bits. For example in a 10 bit converter with 5V as the reference voltage, 1111111111 (all bits one, the highest possible 10 bit binary number) correspond to 5V and 0000000000 (the lowest number corresponds to 0V. Of course, no ADC is absolute, so the voltage mapped to the maximum binary value is called the reference voltage. Here are some important features of ADCs, while going through them we’ll learn how they work. Something in between the logic and the analog input voltage needs to act like an interface. Of course, registers can only accept logic levels themselves as inputs, so if you were to connect the signal directly to a logic input the results wouldn’t be good.
#How does an analog to digital converter work series
What we need is something that can convert a voltage to a series of logic levels, for example in a register. Scaling is basically mapping values from one range to another, so an ADC maps a voltage value to a binary number. Instead we use an ADC to convert the analog voltage input to a series of bits that can be directly connected to the data bus of the microprocessor and used for computation.Ī good way to look at the working of an ADC is to imagine it as a mathematical scaler. If we directly connect this to a digital input, it will register either as a high or a low depending on the input thresholds, which is completely useless.
#How does an analog to digital converter work full
Unfortunately for digital systems, the world we live in is still analog and full of colour, not just black and white.įor example a temperature sensor like the LM35 outputs a voltage dependent on the temperature, in the case of that specific device 10mV per degree rise in temperature.
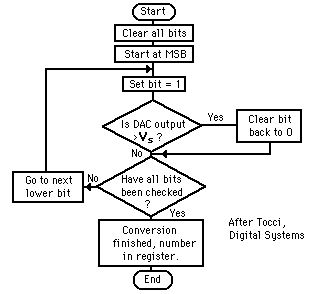
Modern day electronics is purely digital – gone are the good old days of analog computers. These ADC circuits can be found as an individual ADC ICs by themselves or embedded into a microcontroller.
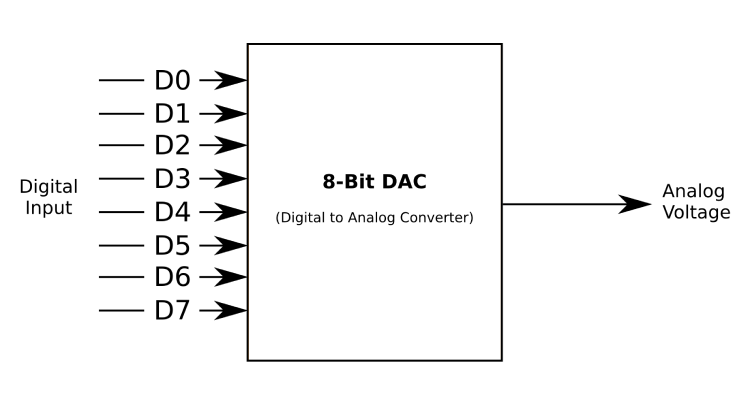
What is an ADC (Analog to Digital Converter)?Īn analog to digital converter is a circuit that converts a continuous voltage value (analog) to a binary value (digital) that can be understood by a digital device which could then be used for digital computation. This something is called the ADC or Analog to Digital Converter and in this ADC article we will learn more about them. So, it is obvious that we need something that could convert these analog parameters to digital value for a microcontroller or micro-processor to understand it. But most of the electronic devices around us starting from a simple digital watch to a super computer are all digital devices.

Everything we see, feel or measure is analog in nature such as light, temperature, speed, pressure etc. We live in an analog world, surrounded by digital devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
